Crohn’s disease
Crohn’s disease is an idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease that can adversely affect a person’s health.
While medication is often the first treatment option, many people with Crohn’s disease eventually need surgery:
- Some patients may choose to have surgery to improve their quality of life.
- For others, surgery is necessary to avoid dangerous complications of Crohn’s disease.
Dr. Konstantinidis and his Surgical Team have extensive experience in treating benign bowel conditions, such as Crohn’s disease, using a robotic system (da Vinci XI) that ensures optimal medical outcomes combined with the lowest possible risk of complications and discomfort to the patient.
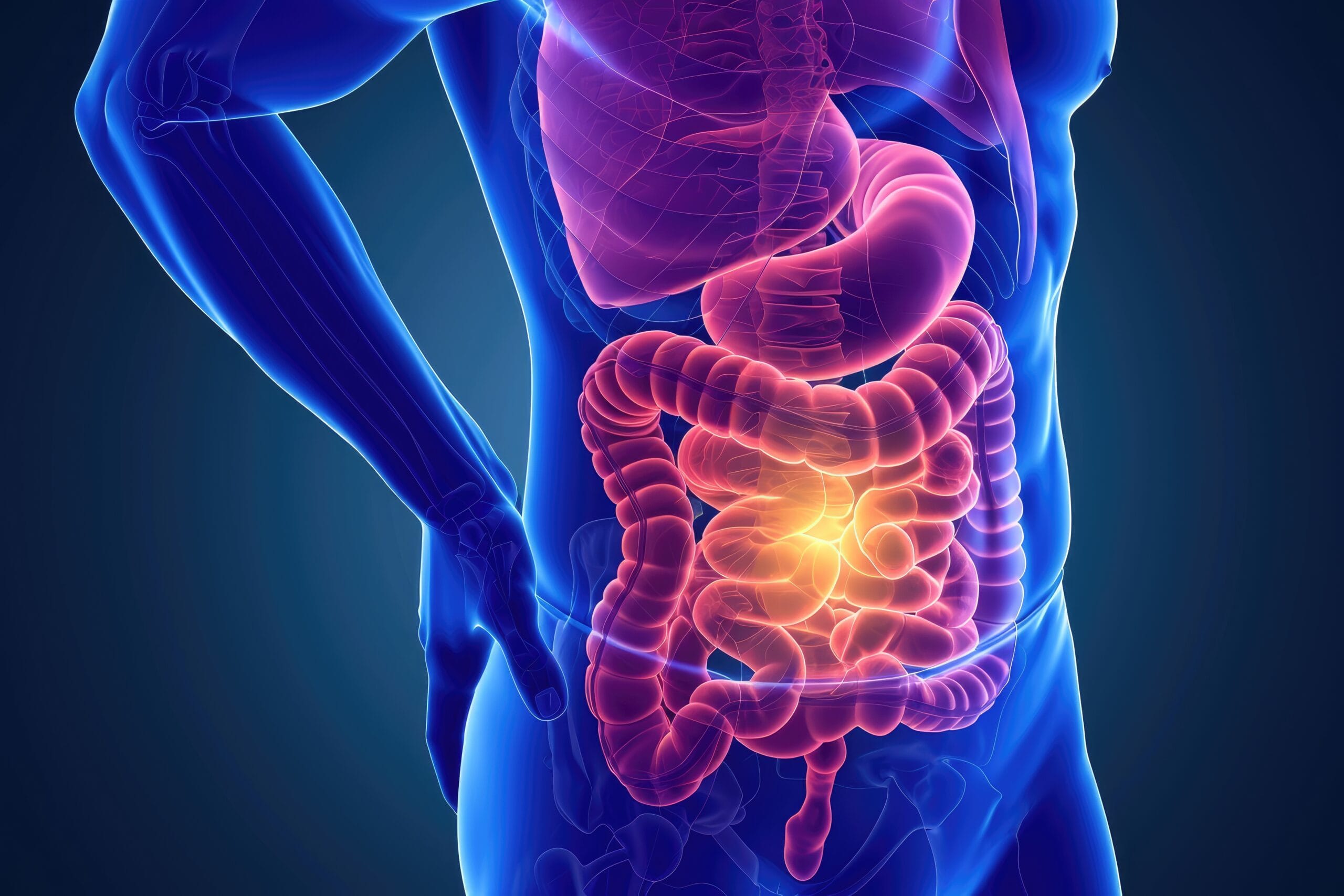
What is Crohn’s Disease?
Crohn’s disease is a chronic idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease.
Inflammation can affect any part of the digestive system, from the mouth to the anus, but it most often occurs in the last part of the small intestine (final ileum) or large intestine.
It is a painful condition that can cause diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea and loss of appetite.
Why choose Dr. Konstantinidis?
Dr. K. M. Konstantinidis and his team possess vast experience in the field of laparoscopic and robotic surgery.
Dr. Konstantinidis is the pioneer of Robotic Surgery in Greece and one of the leading figures internationally in the field, having performed the largest series of General Surgery operations in Europe with the innovative Da Vinci® robotic system, including inguinal hernia surgeries.
What are the symptoms of Crohn’s Disease?
The extent and severity of Crohn’s disease symptoms vary from person to person.
Symptoms of Crohn’s disease include:
abdominal pain
diarrhea
bleeding from the rectum
weight loss
arthritis
skin problems
fever
Rectal bleeding can be severe and continuous enough to cause anemia (low red blood cells).
When does Crohn’s Disease appear?
Crohn’s disease is a rare disease that can affect people of all ages, even children.
However, the disease usually first appears between the ages of 16 and 30.
Also, many cases develop between the ages of 60 and 80.
Crohn’s disease tends to affect slightly more women than men, but in children it is boys that are more affected rather than girls.
What Causes Crohn’s Disease?
The exact causes of Crohn’s disease are unknown. However, scientific research contributes to a combination of factors that may be responsible, such as:
- heredity
- disorders of the immune system
- previous infection
- smoking
- environmental factors
What are the complications of Crohn’s Disease?
Over time, inflammation can damage parts of the digestive system, resulting in complications such as intestinal stenosis or fistula formation. These problems usually require surgery.
How is Crohn’s Disease diagnosed?
The first step in diagnosing Crohn’s disease is a thorough physical examination by a doctor, combined with a series of tests, such as:
- blood tests to check for possible anemia (low red blood cells) or high white blood cells and a rate of sedimentation that is a sign of swelling (inflammation) in the body.
- stool analysis to check for bleeding or infection
- endoscopic examination of the upper and lower digestive tract
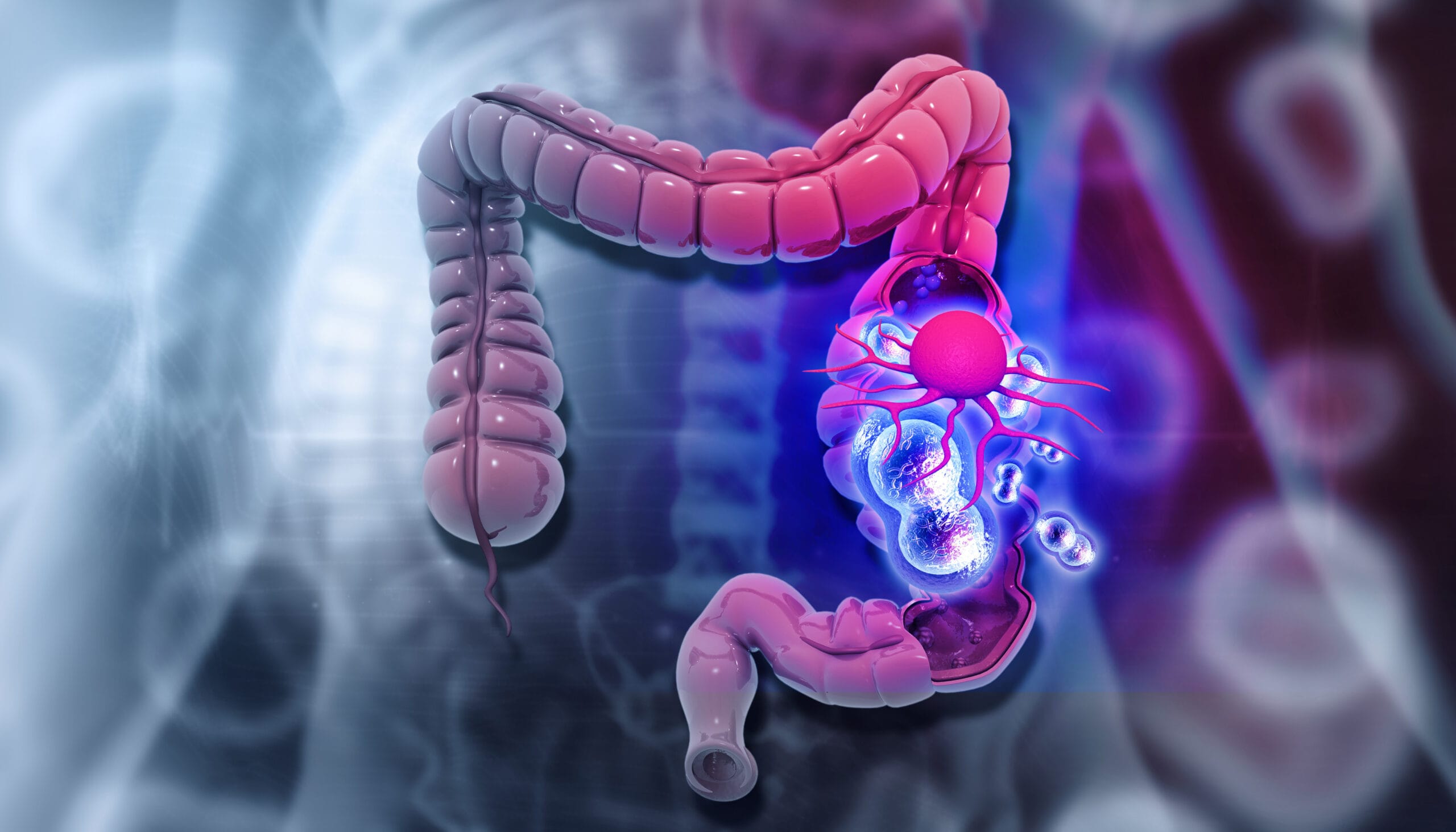
How is Crohn’s Disease treated?
The first line of defense against Crohn’s disease is usually conservative treatment with special medication, which aims to reduce and suppress inflammation, prevent or exacerbate symptoms, and keep the disease in remission.
However, very often surgery is considered necessary if patients do not respond to medication, have or want to avoid dangerous side effects or simply want to improve their quality of life.
Surgical treatment consists of the removal of the affected part of the intestine (enterectomy), as well as the treatment of individual complications of the disease, such as intestinal obstruction or any fistulas that may develop as a result of inflammation.
Small Intestine Enterectomy
What is a Small Intestine Enterectomy?
Perhaps the most common operation on the small intestine is a so-called enterectomy, which refers to the removal of a damaged part of an intestinal condition, such as Crohn’s disease.
After excision of the affected part, an anastomosis is performed, i.e. a union of the remaining small intestine to restore the natural continuity of the digestive tract.
Enterectomy can be performed with open surgery, which involves a large incision, or with some minimally invasive technique, such as laparoscopy and its development: robotic surgery.
What is Laparoscopic Enterectomy?
Laparoscopic enterectomy is a minimally invasive method, which is performed through small holes that are opened in the patient’s abdomen and through which special, thin laparoscopic tools are inserted.
One of them carries a microscope (endoscope) through which the surgeon identifies that part of the small intestine that is diseased and needs to be removed.
After carefully removing the affected part, the remaining intestine is anastomosed with the use of special suturing tools.
What is Robotic Enterectomy?
Robotic small bowel enterectomy maximizes the advantages of a minimally invasive and non-traumatic technique, without the technical difficulties that accompany the conventional laparoscopic method and the great toll of open surgery.
The Surgical Team of Dr. Konstantinidis has been performing robotic enterectomy procedures for many years at Athens Medical Center and now with the state-of-the-art robotic system, Da Vinci Xi.
To date, the team’s experience confirms that the robotic system significantly facilitates the recognition of the anatomy, the mobilization and preparation of the intestine and the avoidance of dangerous complications during the operation.
What are the advantages of Robotic Enterectomy?
Robotic enterectomy is a minimally invasive method and is accompanied by all the relevant advantages, such as:
- less postoperative pain
- minimal blood loss
- shorter hospital stay
- fast recovery and return to daily activities
- optimal cosmetic result
Its most important advantage, however, is that robotic enterectomy minimizes the risk of complications and the toll on the patient’s body.
Due to the high image clarity provided by the robotic system, as well as the unparalleled precision and ease of movement of the robotic arms, the surgeon can move comfortably even in the most inaccessible and difficult anatomical areas.
These anatomical areas can be approached safely without bleeding events and with the assistance of the robot it is possible to remove the affected part of the intestine without unnecessary injury to healthy tissues.
At the same time, thanks to the high accuracy of the robotic movements, it is possible to perform demanding anastomoses with maximum safety and effectiveness.
Obstructive Ileus – Ileal Adhesions Lysis
What is the Obstructive Ileus – Ileal Adhesions Lysis?
Ileus is the condition in which the contents of the intestine cannot be normally advanced into the gastrointestinal tract, due to an obstruction in the small or large intestine.
Ileus may be due to adhesions from previous operations (ileal adhesion), a tumor in the large intestine or inflammation caused by a benign bowel disease (obstructive ileus).
In many cases of the disease the treatment is surgical and concerns the lysis of the congenital or obstructive ileus.
The procedure can be performed with open surgery and open incision -which involves more pain and a higher risk of further adhesions postoperatively- as well as with minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopy and its evolution, robotic surgery.
The method of choice is the laparoscopic or robotic lysis of the adhesive-obstructive ileus. Performing a minimally invasive technique ensures the highest degree of accuracy, flexibility and stability of surgical movements, and minimizes the risk of new adhesions and other complications.