Umbilical hernia
Umbilical hernia, like inguinal hernia, is one of the most common forms of hernia. During its development, the contents of the abdomen, i.e. part of the intestine or fat, are bulging in the umbilical region through a weakness in the abdominal wall. Umbilical hernia appears in infants, children and adults.
Dr. Konstantinidis and his Surgical Team can treat the hernia easily and with absolute safety, thanks to the state-of-the-art robotic system Da Vinci® at Athens Medical Center, which offers impressive results and the lowest complication rates.
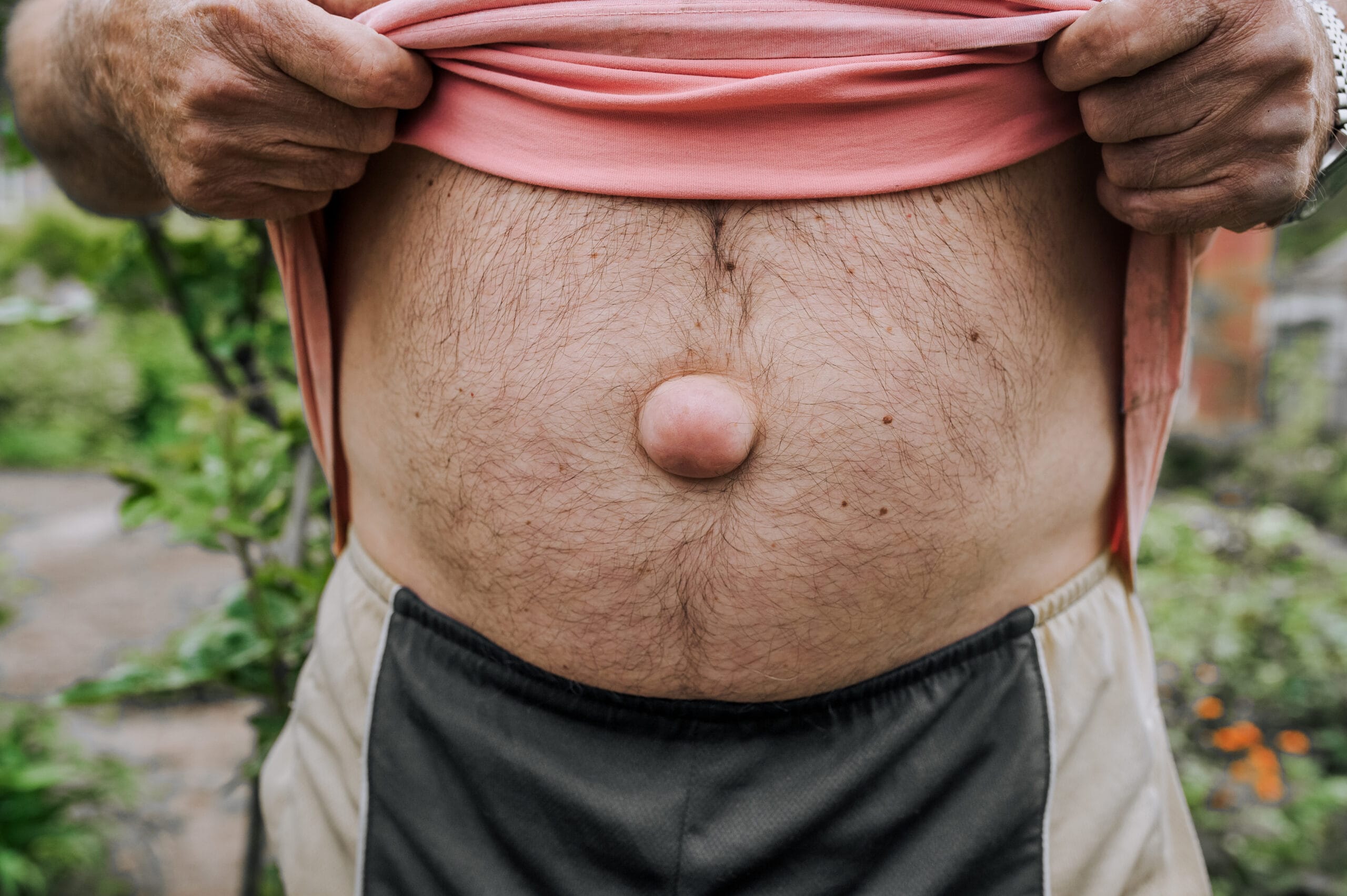
What is an Umbilical Hernia?
Umbilical hernia is the second most common form of hernia after inguinal hernia. It basically appears in the navel area in the form of a bulge. Umbilical hernia occurs when due to the weakness of the abdominal wall a hole is created through which the contents of the abdomen bulge. Umbilical hernia is most common in infants, young children, and women of childbearing potential after childbirth.
It is important that once you notice the umbilical hernia you visit a specialized general surgeon, as it can cause problems, such as pain and obstruction of the viscera, i.e. the ileum.
Why choose Dr. Konstantinidis?
Dr. K. M. Konstantinidis and his team possess vast experience in the field of laparoscopic and robotic surgery.
Dr. Konstantinidis is the pioneer of Robotic Surgery in Greece and one of the leading figures internationally in the field, having performed the largest series of General Surgery operations in Europe with the innovative Da Vinci® robotic system, including inguinal hernia surgeries.
What are the symptoms of Umbilical Hernia?
The most basic symptom of an umbilical hernia is a bulge in the umbilical region.
Other equally serious symptoms include indigestion, pain, heaviness, intestinal and stomach upset.
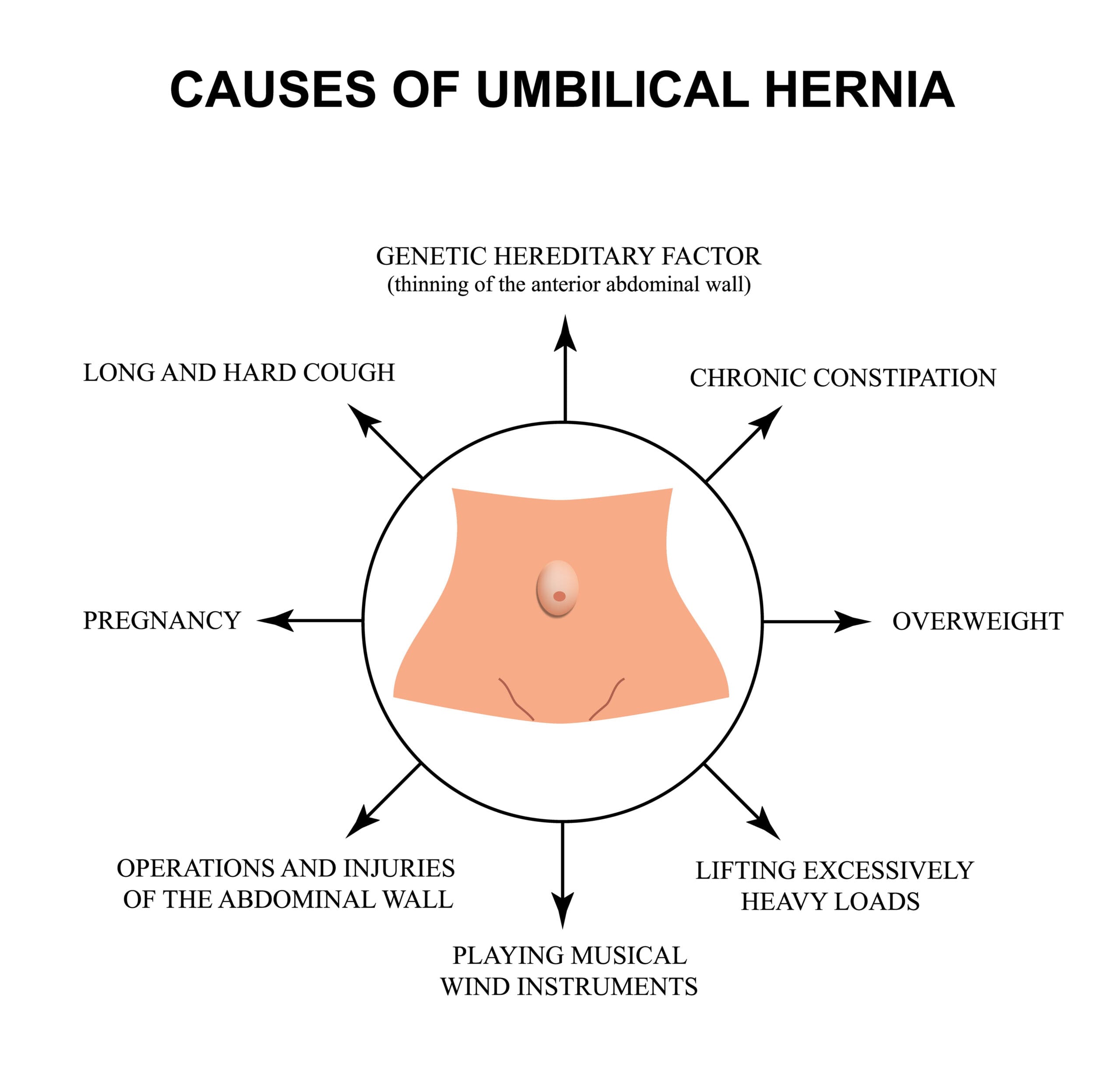
What are the causes of Umbilical Hernia?
Umbilical hernia is a common hernia and can affect anyone, adults, infants and children. In adults it is occurs as a result of a progressive relaxation and opening of the abdominal walls around the navel.
The main causes include obesity, multiple pregnancies, increased intra-abdominal pressure, the presence of intra-abdominal fluid, persistent cough and severe weight loss.
Also, people who have undertaken heavy manual work are particularly prone to the occurrence of umbilical hernia.
When is surgery necessary for the treatment of Umbilical Hernia?
An umbilical hernia alters the shape of the umbilicus and that is why it is relatively easy to diagnose through a clinical examination by a specialized doctor. A key point of the examination is the determination of the width of the opening of the muscle wall, which defines the treatment approach that will be followed.
Treatment of an umbilical hernia is carried out surgically with the method of laparoscopy and placement of a mesh.
A visit to a specialized general surgeon is necessary, since one of the most important complications of the umbilical hernia is the strangulation of the viscera it contains. If the umbilical hernia is not treated in time, it can cause ischemia or necrosis of the organ with serious consequences.
Is Umbilical Hernia treated laparoscopically?
Umbilical hernia is treated surgically with general anesthesia, using the laparoscopic method. The restoration of the hernia is achieved by placing a mesh. Laparoscopic surgery is one of the most modern methods and has many advantages, including:
- Minimization of incisions
- Less postoperative pain
- Shorter hospital stay
- Avoidance of postoperative inflammations and infections
In addition to the laparoscopic method, robotic surgery can also be applied, which in essence is an evolution of laparoscopic with still more benefits for the patient both during surgery and recovery.
What do I need to know about surgery? Are there any complications?
Both laparoscopic and robotic surgery are completely safe. Patients show practically zero postoperative complications and infections and are bloodless as they are minimally invasive procedures. The tissues are not injured, there is immediate recovery and no scars are left.
After the operation, the patient recovers immediately and is mobilized on the same day.
The duration of hospitalization is short and the patient can go home the next day with instructions with regards to food intake, mild antibiotics and analgesia.
Postoperative recovery is very fast, as due to the exceptional accuracy of movements of the Da Vinci® robotic system, the injury of the surrounding tissues is minimized.
The patient can return to work and daily activities a few days after surgery, while the use of a light postoperative abdominal band is recommended.
What is the cost of the operation?
Some patients worry if they can afford robotic surgery. However, although it is more expensive as an operation, the total cost robotic surgery including that of hospitalization is ultimately the same that of more conventional approaches, since this method minimizes the possibility of postoperative complications and reduces the time spent in the hospital.