Gynecological Cancers
Dr. Konstantinidis leads a team of world-class specialists, using the most innovative treatments and surgical approaches, such as the use of the state-of-the-art da Vinci Xi robotic surgery system at Athens Medical Center, for the treatment of women diagnosed with gynecological cancer.
From the first moment, Dr. Konstantinidis and his Surgical Team will work closely with you and your loved ones, with the aim of developing a personalized and integrated approach to cancer treatment, prioritizing not just survival but also well-being, fertility and normal sexual function.
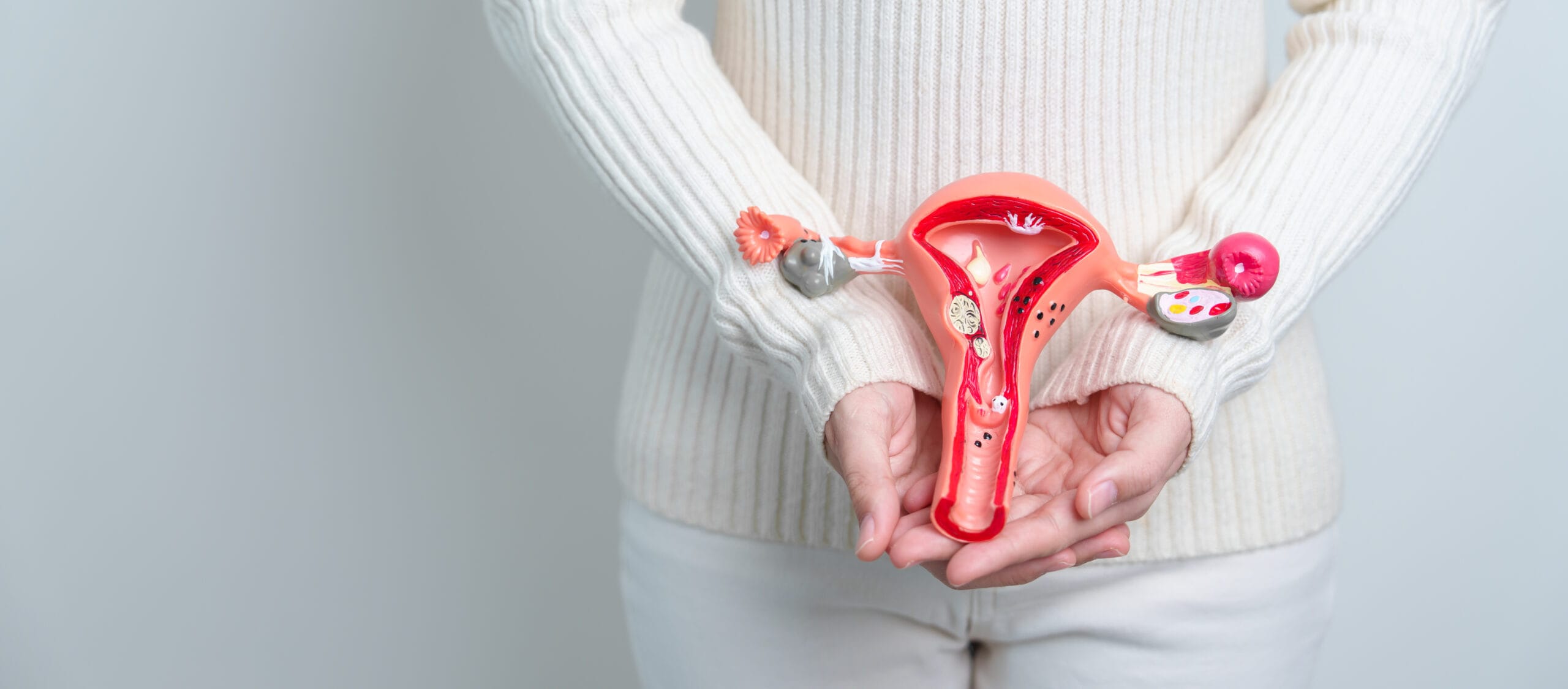
What is Gynecological Cancer and what types are there?
The term gynecological cancer refers to any type of malignancy that has the reproductive organs of a woman as a starting point.
There are five main types of gynecological cancer:
- endometrial or uterine cancer
- cervical cancer
- ovarian cancer
- vaginal cancer
- vulvar cancer
There are also rarer types of gynecological malignancy, such as fallopian tube cancer.
Why choose Dr. Konstantinidis?
Dr. K. M. Konstantinidis and his team possess vast experience in the field of laparoscopic and robotic surgery.
Dr. Konstantinidis is the pioneer of Robotic Surgery in Greece and one of the leading figures internationally in the field, having performed the largest series of General Surgery operations in Europe with the innovative Da Vinci® robotic system, including inguinal hernia surgeries.
What is Endometrial / Uterine Cancer?
This type of cancer is often referred to as uterine cancer, although it is not exactly the same thing: endometrial cancer develops in the inner lining of the uterus.
The most common symptoms of endometrial cancer are the following:
- abnormal vaginal bleeding
- painful urination
- an enlarged uterus, which the doctor can detect during an examination
- pain during sexual intercourse
- unexplained weight loss
What is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer occurs when cancer cells grow and multiply on the surface of the cervix, which is located at the bottom of the uterus, at the point where it connects to the vagina.
One of the most common causes of this type of cancer is human papillomavirus or HPV.
If detected early, cervical cancer can be successfully treated.
The best way to prevent and / or detect cervical cancer is to have a regular gynecological examination.
Understanding the first symptoms also helps to ensure effective treatment.
The most common symptoms are:
- irregular bleeding, such as spots between or periods
- menstrual bleeding that is greater or heavier than normal
- persistent pain in the pelvis or back
- vaginal secretions
- pain during intercourse
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer usually starts in the ovaries, but recent research shows that it can actually grow in other reproductive organs, such as the fallopian tubes.
The ovaries produce eggs, which are made up of three types of cells, each of which can develop a different type of tumor:
- Epithelial tumors form in the cells that cover the surface of the ovaries and are the most common form of ovarian tumors.
- Non-epithelial tumors grow in either the reproductive cells or the connective tissue stromal cells around the ovary.
Three out of four ovarian tumors are benign.
At an early stage, malignancies rarely give symptoms, which usually occur when the cancer is more advanced. The most common symptoms include:
- pain in the pelvis, back or abdomen
- bloating
- loss of appetite
- urgent need to urinate
- constipation
- pain during intercourse
How is Gynecological Cancer diagnosed?
The diagnosis of gynecological cancer varies depending on the type of malignancy:
- Diagnosis of endometrial / uterine cancer: Endometrial or uterine cancer can be confirmed with minimally invasive tests, such as endometrial biopsy, vaginal ultrasound, and hysteroscopy. Once the cancer has been confirmed, several tests can be carried out, such as blood tests, a chest x-ray and cervical ultrasound, as well as a CT scan. Positron emission tomography in combination with computed tomography (PET / CT) helps to detect possible metastases.
- Diagnosis of cervical cancer: It includes colposcopy and biopsy, usually after a positive and high-risk result of a test for HPV.
- Diagnosis of ovarian cancer: Measurement of CA 125 and carcinoembryonic antigen in serum helps in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer in combination with conventional imaging methods such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) and transvaginal ultrasound.
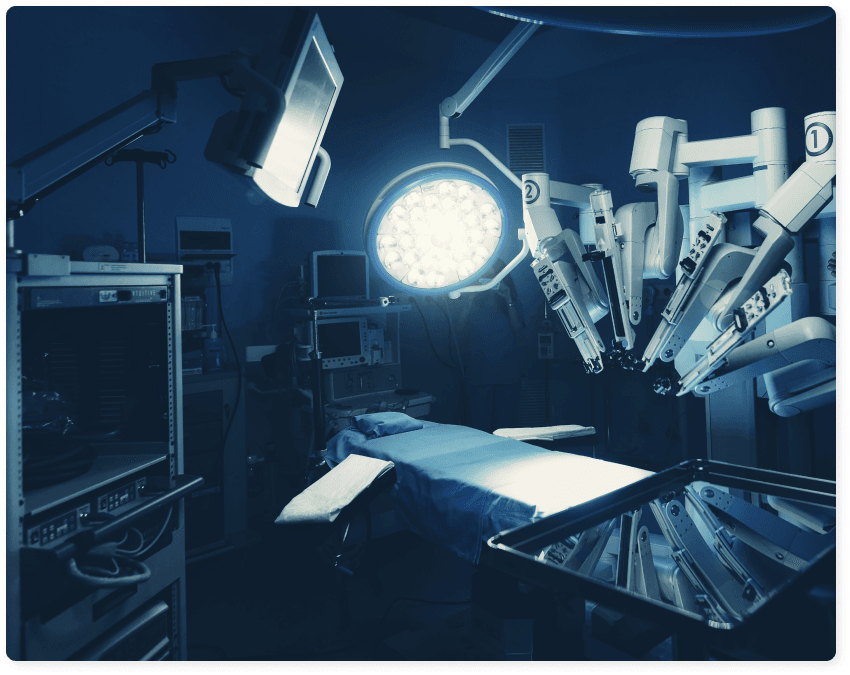
Treatment – How is Gynecological Cancer treated?
Depending on the type and stage of gynecological cancer, the relevant treatment plan is determined, which focuses on the surgical removal of the tumor.
In recent years, minimally invasive surgical techniques have gained ground, in order to minimize the pain and suffering of patients, as well as the risk of complications, which is higher in open surgery.
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive technique that significantly reduces hospital stay, postoperative pain and recovery time, while offering excellent oncological outcomes.
Robotic surgery has the same advantages as advanced laparoscopy, in addition allowing surgeons to operate with increased accuracy, stability and flexibility. As a result, they perform surgery more easily, efficiently and safely.
The most common types of surgery to treat gynecological cancers are:
- hysterectomy, which involves the removal of the uterus and cervix
- total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, i.e. removal of all internal reproductive organs
Other types of gynecological cancer treatment that can be combined with surgery include:
- intraperitoneal chemotherapy, i.e. chemotherapy with laparoscopic intraperitoneal hyperthermia (especially for the treatment of advanced ovarian cancer)
- systemic chemotherapy
- radiotherapy
- hormone therapy
TOTAL INTERNAL REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS REMOVAL WITH RADICAL LYMPH NODE DISSECTION
What Is Total Internal Reproductive Organs Removal with Radical Lymph Node Dissection?
In some cases of gynecological cancer, especially in the endometrium, uterus or cervix, appropriate treatment may involve the total removal of the internal reproductive organs as well as the adjacent lymph nodes.
In this procedure, the uterus and the adjacent organs (ovaries, fallopian tubes) and tissues are removed in order to prevent further spreading of the cancer.
The use of a surgical robot constitutes this procedure minimally invasive and allows maximum accuracy, stability and flexibility in movements. This is an important advantage, especially in those cases where, after histopathological examination of the surrounding lymph nodes in real time during the operation, radical lymph node dissection is required.